Understanding your blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of managing your health, especially if you live with diabetes or are at risk. High or low blood sugar can lead to serious health complications over time, impacting everything from your energy levels to your long-term organ health.
Regular blood sugar testing empowers you with vital information. It helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication, putting you in control of your well-being. This guide delves into why, when, and how you should monitor your blood sugar, ensuring you have the knowledge to navigate this crucial aspect of your health journey.
Table of Contents
- Why is Blood Sugar Testing So Important?
- Who Needs to Test Their Blood Sugar?
- When Should You Test Your Blood Sugar?
- How to Perform a Home Blood Sugar Test
- Interpreting Your Blood Sugar Results
Why is Blood Sugar Testing So Important?
Regular blood sugar testing offers invaluable insights into your metabolic health. It is not just for those with diabetes; it’s a proactive step for anyone seeking to understand and optimize their body’s function.
For Diabetes Management
If you have diabetes, consistent blood sugar monitoring becomes a critical tool. It helps you understand how your body reacts to various foods, physical activities, and medications. This data allows you to make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, preventing both dangerously high (hyperglycemia) and low (hypoglycemia) blood sugar episodes.
Furthermore, effective management reduces your risk of long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, and vision loss. Tracking your levels empowers you to maintain stable blood sugar and a healthier life.
For Early Detection and Prevention
Even without a diabetes diagnosis, periodic blood sugar tests can detect pre-diabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be type 2 diabetes. Catching this early provides a crucial window to implement lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, potentially reversing the condition and preventing full-blown diabetes.
Understanding Your Body’s Response
Blood sugar testing reveals how different factors influence your glucose levels. You learn how specific meals, stress, illnesses, or even a good night’s sleep affect your body. This personalized understanding allows you to tailor your daily habits for optimal health and better energy.
Who Needs to Test Their Blood Sugar?
While often associated with diabetes, various groups benefit significantly from regular blood sugar monitoring. Understanding who should test helps individuals take proactive steps towards better health.
Individuals with Diagnosed Diabetes
This group includes people with Type 1, Type 2, and other specific types of diabetes. Frequent testing helps them manage their condition, adjust medication, and prevent complications. The frequency of testing depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment regimen.
Those with Pre-diabetes
If a doctor has diagnosed you with pre-diabetes, regular testing helps you monitor the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions. It provides motivation and feedback on whether your efforts are helping to normalize your glucose levels.
People at High Risk for Diabetes
Individuals with risk factors like a family history of diabetes, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, or certain ethnic backgrounds should consider periodic blood sugar checks. Early detection can lead to preventative action.
During Pregnancy (Gestational Diabetes)
Pregnant women may develop gestational diabetes, which can impact both maternal and fetal health. Regular blood sugar testing is essential for managing this condition, often involving dietary changes and, in some cases, insulin. Monitoring helps ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
When Should You Test Your Blood Sugar?
The timing of your blood sugar tests significantly impacts the information you gather. Different times reveal different aspects of your metabolic control.
Fasting Blood Sugar
You test fasting blood sugar after not eating or drinking anything (except water) for at least 8 hours, typically first thing in the morning. This measurement gives you a baseline of your glucose levels and reflects how your body produces and processes glucose overnight.
Before and After Meals
Testing before a meal indicates your pre-meal baseline. Testing 1-2 hours after a meal (post-prandial) shows how your body processes carbohydrates and responds to food. This helps identify which foods cause significant spikes in your blood sugar.
Before and After Exercise
Physical activity can dramatically affect blood sugar. Testing before exercise helps you avoid hypoglycemia, especially if you use insulin. Testing afterward shows how your body uses glucose during and after exertion, helping you plan future activities.
Before Bedtime
A blood sugar test before bed helps ensure your levels are stable enough to prevent hypoglycemia during the night. It also provides insight into how your evening meal and activities affected your glucose.
When Feeling Unwell or Stressed
Illness, stress, and certain medications can elevate blood sugar levels. Testing during these times helps you understand these influences and adjust your care plan accordingly. Always consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent high or low readings.
Frequency Based on Diabetes Type and Treatment
The frequency of testing varies greatly. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes, especially those on intensive insulin regimens, may test multiple times a day. People with Type 2 diabetes might test less often, depending on whether they manage their condition with diet, oral medications, or insulin. Your doctor will provide personalized recommendations.
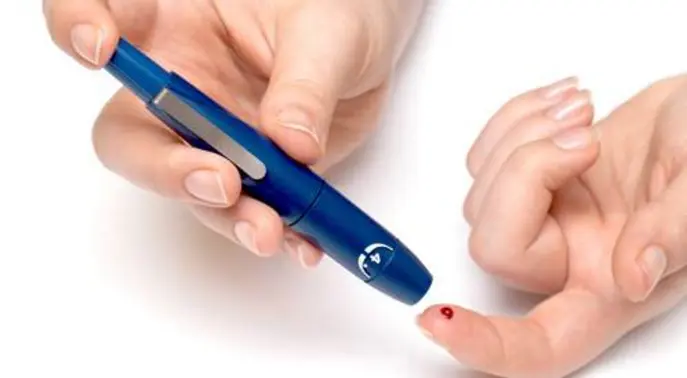
How to Perform a Home Blood Sugar Test
Performing a home blood sugar test is a straightforward process, empowering you to gain immediate insights into your glucose levels. While devices vary, the basic steps remain similar.
What You’ll Need
- Blood glucose meter: Your device for reading the blood sample.
- Test strips: Specific to your meter, these react with the blood.
- Lancets: Small, sterile needles for pricking your finger.
- Lancing device: Holds the lancet and helps you prick your finger safely.
- Alcohol swab: To clean the test site (optional, but good practice).
- Blood sugar logbook or app: To record your results.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Wash your hands: Use warm, soapy water and dry them thoroughly. This cleans the skin and helps increase blood flow.
- Prepare your lancing device: Insert a fresh lancet into the device according to its instructions. Adjust the depth setting if needed.
- Insert a test strip: Place a test strip into your blood glucose meter. Your meter will likely turn on automatically.
- Prick your finger: Press the lancing device firmly against the side of your fingertip (avoid the very tip). Press the release button.
- Obtain a blood sample: Gently squeeze your finger from the base towards the tip until a small drop of blood forms. Do not smear the blood.
- Apply blood to the strip: Touch the edge of the test strip to the blood drop. The strip will draw the blood in.
- Read the results: Your meter will display your blood sugar reading within seconds.
- Record your results: Note the reading, date, and time in your logbook or app.
- Dispose of sharps: Safely discard the used lancet and test strip in a sharps container.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
For some individuals, especially those with Type 1 diabetes or specific needs, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) offer an alternative to traditional finger-prick tests. A small sensor, typically worn on the arm or abdomen, continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid just under the skin. It sends data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone, providing real-time readings and trend arrows. CGMs offer a comprehensive view of glucose fluctuations throughout the day and night, without frequent finger pricks.
Interpreting Your Blood Sugar Results
Understanding what your blood sugar numbers mean is crucial for effective health management. Your doctor will provide personalized target ranges, but general guidelines exist.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
- Fasting: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
- 2 hours after eating: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
Pre-diabetes Ranges
- Fasting: 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L)
- 2 hours after eating: 140-199 mg/dL (7.8-11.0 mmol/L)
Diabetes Ranges
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests
- 2 hours after eating: 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher
Please note that these are general guidelines, and individual targets can vary based on age, other health conditions, and personal circumstances. Always discuss your specific target ranges with your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If your blood sugar readings consistently fall outside your target range, are extremely high (e.g., above 240 mg/dL) or extremely low (e.g., below 70 mg/dL), or if you experience symptoms like dizziness, confusion, excessive thirst, or frequent urination, contact your doctor immediately. These could indicate a need for adjustments to your treatment plan or an underlying issue.
Conclusion
The blood sugar test is more than just a medical procedure; it’s a powerful tool for personal health empowerment. By understanding why, when, and how to monitor your glucose levels, you gain the knowledge to make proactive choices that safeguard your well-being. Regular testing allows you to observe your body’s unique responses, fine-tune your lifestyle, and collaborate effectively with your healthcare team.
Embrace this essential practice. It’s a key step towards maintaining stable blood sugar, preventing complications, and living a healthier, more vibrant life.